The aim of the study is to identify cornulin (CRNN) protein expression associated with advancement of tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC). A comparison of addictive (containing potential carcinogens) versus non-addiction causative agents was expected to allow detection of differences in CRNN expression associated with TSCC. Bespoke tissue microarrays (TMAs) were prepared and immunohistochemistry (IHC) performed to determine the changes in CRNN expression in epithelial cells of node-negative (pN-), node-positive (pN ) TSCC and non-cancer patients’ oral tissues. TMAs were validated by performing IHC on whole diagnostic tissues. Chi-square test or Fisher’s-exact tests were used to establish significant expression differences. Analogous analyses were performed for biomarkers previously associated with TSCC, namely collagen I alpha 2 (COL1A2) and decorin (DCN) to compare the significance of CRNN. Keratinisation and its level (low, extensive) were studied in relation to CRNN so that the extent of squamous differentiation could better be assessed.
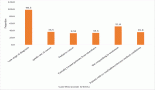
IHC immunoreactive score (IRS) clustered the patients based on weak/moderate (Low (IRS ≤ 3)) or strong (High (IRS ≥ 4)) expression groups. A low expression was observed in a larger number of patients in control proteins COL1A2 (77.3%), DCN (87.5%) and target protein CRNN (52.3%), respectively. Low CRNN expression was observed in TSCC where nodes were involved (pN : mean 1.4 ± 2.1) (p = 0.248). Keratinisation (%) was low (0% ≤ 50%) in 42.2% and extensive (1% ≥ 50.0%) in 57.8% patients. In conclusion, our study suggested that Low CRNN expression was associated with grade and lymph node metastasis in TSCC. CRNN expression is independent of addiction, however potentially carcinogenic addictive substances might be aiding in the disease progression.