Accurate measurement of breast tumour size determines staging and prognosis. Discrepancies amongst clinical examination (CE), ultrasonography (USG), mammography, pathological examination (PE) and magnetic resonance imaging have been reported. However, few studies have evaluated changes in breast tumour size from the operating table to the laboratory.
Objectives and methods: A prospective study was designed to assess the intra-operative (IO) tumour size in 29 patients of breast cancer presenting to a tertiary care centre in Delhi and to compare it with CE, USG and PE.
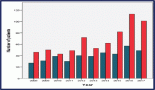
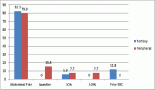
Observations and results: Twenty-nine patients (mean age: 47 years), presenting with invasive duct carcinoma (stage IIIA: 31%, stage IIB: 28%), were included in the study. Comparison with mean IO (4.2 cm) revealed that both USG and PE underestimated tumour size by a mean of 0.35 cm (8.4%) and 0.45 cm (10.7%), respectively, in most patients. CE tended to overestimate size by 0.82 cm (19.8%). All three modalities showed statistically significant correlation with IO (maximum Pearson's correlation coefficient for PE=0.937, p<0.001; R2=0.877, maximum for PE). Two-way analysis of variance revealed mean difference in size to be statistically significant (p=0.000) only between CE and IO.
Discussion: Formalin processing causes changes in tumour dimensions in the breast, causing reduction in tumour size. It may also have a bearing on the assessment of surgical margins in breast conservation surgery. Immediate post-operative measurement of the specimen is ideal. Protocols for specimen fixation should be standardised.