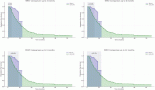
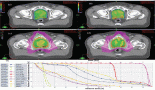
Cervical cancer is common among women in the Indian subcontinent and the incidences and death rates are gradually increasing over the years. Several dietary phytochemicals have been reported to have growth inhibitory and apoptotic effect on HeLa and other cervical cell lines. In this study, using Hoechst 33342 staining, MTT, Annexin V-FLUOS/PI and TUNEL assays we demonstrated that Syzygium cumini extract inhibits the growth and induces apoptosis in HeLa and SiHa cervical cancer cell lines in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The phytochemical, its mode of action and safety issues are yet to be determined.