Background and purpose: A high-quality treatment planning process is crucial in advanced radiotherapy techniques to ensure adequate dose to the target volume (TV) and sparing of organs at risk (OARs). This process often requires intensive labour, creating barriers for deployment in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). We aimed to establish the feasibility of implementing knowledge-based auto-planning to facilitate clinical efficiency and increase patient throughput in an LMIC.
Materials and methods: We evaluated 60 randomly selected VMAT manual plans (VMPs), including 10 for each of the following sites: head and neck, oesophagus, breast, prostate, cervical, and rectal cancers. Using the same CT-structure datasets, volumetric modulated arc therapy auto-plans (VAPs), which involved matching the patient’s CT-structure datasets with corresponding model structures before optimisation, were generated using RapidPlan® knowledge-based models. The plans were compared using different dosimetric parameters, average planning times (APT) and plan scores, the latter of which was used for quantification of plan quality.
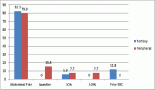
Results: The APT was 29.5 ± 3.0 minutes for VAPs compared to 43.2 ± 12.0 minutes for VMPs (p < 0.01), an approximate 33.0% time saving. The average plan scores were 73.9% ± 9.5% and 74.8% ± 10.5% for VAPs and VMPs, respectively (p = 0.50). The average homogeneity and conformity indices were 0.12 ± 0.05 and 0.93 ± 0.04 for VAPs compared to 0.09 ± 0.04 and 0.94 ± 0.03 for VMPs, respectively. For prostate and breast cases, both methods achieved the rectum’s V50Gy ≤ 50% and spinal cord’s Dmax ≤ 39.0 Gy constraints; however, VAPs projected lower doses than the corresponding VMPs (16.5 ± 4.3 versus 30.6 ± 13.1: p = 0.01) and (6.0 ± 1.6 versus 19.6 ± 2.3: p < 0.01).
Conclusion: The knowledge-based VAP-generated technique offers adequate dose coverage, homogeneity and conformity to the TV while sparing OARs, is less dependent on the planner’s experience, saves planning time and holds tremendous potential for improving radiotherapy workflow in LMICs.