Introduction: Breast cancer (BC) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Owing to early diagnosis and better therapeutic care, survivorship in these patients have improved tremendously. Chemotherapy, cornerstone in BC management have been associated with debilitating side effects including the effect on cognitive function, which significantly impairs the quality of life in these patients. Thus, it is imperative to understand the timeline and magnitude of the effects of chemotherapy on cognition to develop better management strategies. This is even more relevant in developing country like India, where there is inconspicuous absence of data in this regard.
Aim: To study the acute and long-term effects of chemotherapy on the cognitive function in BC patients compared to chemotherapy naïve (Cx naïve) BC patients (disease controls) and matched healthy controls (HC) using subjective, objective questionnaires and neuropsychological tests (NPTs).
Methods: The current cross-sectional study involved 120 participants, 30 each of Cx naïve BC patients, during chemotherapy BC patients (during Cx), post-chemotherapy BC patients (post Cx) and HC; all matched for age and education levels. Both subjective and objective assessments of cognitive functions were done in all the groups. Hindi Mental State Examination (HMSE) and FACT Cog questionnaire V3 were used for subjective assessment while Addenbrooke Cognitive Examination-III (ACE-III) questionnaire and domain specific computer based NPT (Wisconsin card sorting task (WCST) (learning), Flanker’s (attention and interference) and n back task (working memory) were done for objective assessment. The data were analysed for descriptive and inferential statistics, as appropriate using GraphPad Prism V9.
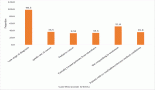
Results: The subjective assessment using HMSE questionnaire revealed a significantly lower score in post Cx group as compared to HC (p < 0.001); however, it was comparable in other groups. FACT Cog V3 questionnaire revealed significantly higher cognitive impairment among those during Cx compared to Cx naïve patients (p < 0.001), post Cx BC patients (p < 0.001) and HC (p < 0.0001). Meanwhile, the objective assessment using ACE-III examination revealed significantly lesser scores among during Cx patients (p < 0.001), and post Cx BC patients (p < 0.0001) compared to HC group. In NPTs, WCST and N back working memory task revealed significantly lower accuracy in Cx naïve versus post Cx (p = 0.0054, p = 0.0068, respectively) and HC versus post Cx (p = 0.0054, p = 0.0045, respectively), while no significant difference was found in Flanker’s task. Furthermore, in WCST there were significantly higher scores present in total reaction time in post Cx compared to Cx naïve: p = 0.00444 and HC: p = 0.0003). In Flanker’s task reaction time was higher in all the groups (Cx naïve: p = 0.002, during Cx: p = 0.0007 and Post Cx: p < 0.0001) compared to HC. In addition negative correlation was found between the duration of chemotherapy with Perceived Cognitive Abilities (r = −0.482; p = 0.006), between the total number of cycles with Fact Cog Total (r = −0.373, p = 0.04) and Perceived Cognitive abilities (r = 0.39, p = 0.03), and between total dose and perceived cognitive abilities (r = −0.42, p = 0.014) also a positive correlation was seen between dose of epirubicin with reaction time of n back (r = 0.373, p = 0.04).
Conclusion: Chemotherapy can have a negative impact on the cognitive function in BC patients, manifested as both acute and long-term effects, based on patient reported/subjective and laboratory based/objective cognitive function tests. The deficits were seen mostly seen in domains of attention and working memory across groups compared to matched HC.