Background: Breast cancer (BC) is prevalent in Sudan, yet data on its epidemiology in Eastern Sudan is limited. This study aims to provide insights into the demographic and clinicopathologic features of BC patients treated at the East Oncology Centre (EOC) in Gadarif State, Eastern Sudan. Furthermore, we aim to identify the factors that contribute to a late-stage diagnosis.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included patients diagnosed with BC and treated in the EOC between 2016 and 2022. Data obtained from medical records were analysed using R software, with descriptive statistics and multiple logistic regressions applied to determine determinants of advanced-stage presentation. A p‐value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
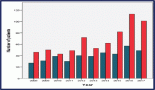
Results: Among the 394 patients studied, the majority were women (96%), married (66%) and from rural areas (43%). The peak years for BC diagnoses were 2018 and 2022, with a median age at diagnosis of 48 years. A family history of cancer was reported by 20% of patients. Clinical stages were distributed as follows: I (1.6%), II (17%), III (50%) and IV (32%). Twenty-five percent tested positive for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, while 73% tested negative and 43% had triple-negative BC. Modified radical mastectomy was performed in 47% of patients, with 21% undergoing breast-conserving surgery. Treatment rates were 38% for radiotherapy, 84% for chemotherapy and 46% for hormonal therapy. Higher grade BC and lower education levels were associated with advanced-stage presentation, while a family history of cancer reduced the risk of advanced-stage disease (OR: 0.38, 95% CI: 0.18–0.78).
Conclusion: The study found that females in East Sudan often present at a young age and advanced stage, with a significant prevalence of triple-negative BC. Notably, family cancer history exhibited a protective effect against advanced-stage presentation, while grade 3 cancer was positively associated with advanced disease.