Purpose: This study evaluates the relationship between geography and ethnicity on the completeness of documentation of diagnostic work-up and treatment modalities in Sudan for patients with breast cancer.
Methods: This retrospective study used data abstracted from patients with breast cancer receiving cancer care at Sudan’s largest cancer centre (Radiation and Isotopes Center Khartoum) in 2017. Patient demographic and clinical characteristics were abstracted from paper medical records. Odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals were estimated to evaluate complete diagnostic work-up on ethnic group, origin and residence using binomial logistic regression models.
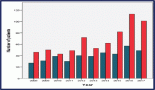
Results: Of 237 patients, the median age was 52 (interquartile range 43–61). Most often patients identified as Arab (68%), originated from Central, Northeastern and Khartoum regions (all 28%) and lived in the Khartoum region (52%). Overall, 49% had incomplete diagnostic work-up, with modest differences by ethnicity and geography. In adjusted analyses, non-statistical differences were found between the ethnic group, geographic origin and residence and having complete diagnostic work-up. For treatment modality, significant differences were observed between receptor status and receiving hormone therapy (p = 0.004). Only 28% of patients with HR+ breast cancer received hormonal therapy. For those with HR− or undocumented breast cancer subtype, 36% and 17% received hormone therapy, respectively.
Conclusion: Approximately half of Sudanese patients with breast cancer had incomplete diagnostic work-up, irrespective of ethnicity and geography. Moreover, a high proportion of patients received inappropriate treatment. This underlines a considerable systems-based quality gap in care delivery, demanding efforts to improve diagnostic work-up for all patients with breast cancer in Sudan.