Introduction: In Ghana, the Papanicolaou (PAP) smear remains central to cervical cancer screening although human papilloma virus testing is recommended. The success of the PAP smear however depends on stringent quality processes. Unfortunately, PAP smear reporting in Ghana is uncoordinated with no clear quality guidelines.
Methods: We applied quality guidelines to all PAP smear diagnoses of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) at Catholic Hospital Battor from 1 June 2016 to 31 August 2021. Available slides were independently reviewed by two pathologists, colposcopy findings were correlated with PAP smear results and histology cytology correlation was carried out after loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP).
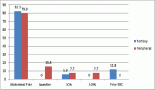
Results: Of 17 women with HSIL, 3 available slides were reviewed and found to be normal (negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy), obviating the need for LEEP. Of the 11 that had LEEP after colposcopy, cytology histology correlation revealed that 54.6% (6) had no dysplasia, 27.3% (3) were cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) II and 18.2% (2) were CIN III. Cytology, colposcopy correlation showed that (out) of the 17 women, 52.9% (9) had no lesions, 29.4% (5) had minor changes and 17.7% (3) had major changes on their cervix. Of the nine that had no lesions on colposcopy, five had LEEP. Of these five, dysplasia (at least CIN II) was revealed in three (60%).
Conclusion: The lack of quality processes in PAP smear reporting results in a high false positive rate with overtreatment of patients. Quality measures need to be adopted for the reporting of PAP smears in Ghana if gains are to be made in the fight against cervical cancer.