Background and rationale: Quality education is a prerequisite for building a sustainable health system. To address this requirement, it is necessary to strengthen capacity and expand the training opportunities to ensure equitable and efficient development of core professional competencies for specific contexts and educational needs.
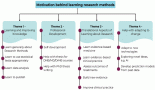
Methods and results: A competency-based training programme for Breast Surgeons was built and was applied based on the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR). This framework provides a pragmatic structure for approaching complex interactions, multi-level and transient constructs in the real world. CFIR guided the implementation process and verified what works, where and why across each step. CFIR guided implementation was through an adaptable approach of the domains and creating relevant constructs that set up an ideal roadmap to analyse and improve learning needs, the curriculum design and the learning environment.
Conclusion: The outcomes described in this manuscript demonstrate that evidence-based principles can be implemented in health professionals’ training and clinical practice even in resource-constrained settings. Building strong and sustainable healthcare workforce capacity is an urgent need for improved health service delivery and addresses real-life workplace needs in low-middle income countries. This programme integrates training with service to solve problems and develop initiatives to address existing local health priorities. While the article focuses on a training programme development, findings are shared to promote dissemination into other settings.