Background: Oncoplastic surgery for breast cancer (OPS) has been a surgical trend for the past 25 years. In 2012, OPS has been introduced as the standard treatment for a selected group of patients at the National Cancer Institute of Peru (INEN). The aim of this study is to describe our findings.
Methods: This is a retrospective and descriptive study that identified demographics, tumour-pathologic features and includes patients solely treated since diagnosis until late follow-up at INEN. These OPS patients were identified from the conservative treatment patients group by review of medical charts and creation of a database for periods December 2005 through December 2015.
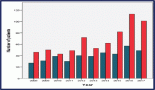
Results: A total of 146 patients were ruled in by the inclusion criteria. All patients were Peruvian females, 56.2% being 51 or older. 93.8% had core biopsy diagnosis of breast cancer and 52.1% located at the upper outer quadrant. 79.5% patients had upfront OPS and the round block (43.2%) and reduction/mastopexy (23.3%) were the most used techniques. pT2 was the most frequent size (54.7%). We achieved negative margins in 134 patients (93.2%) in a single procedure. Of 29 patients, who had neoadjuvant treatment, 11 achieved pCR. Only 5.5% had pN2 or higher. 95.2% received complimentary external beam radiotherapy.
Conclusions: OPS has proven to be a reliable surgical option, both for aesthetic and oncologic outcomes. Important points for achieving these results are breast surgeons having properly trained under the OPS philosophy and knowing the patients’ characteristics for correct technique selection.