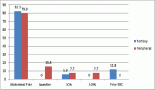
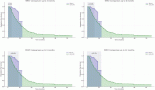
With the great advances made in the treatment and prevention of infectious diseases over the last century, chronic degenerative diseases—cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and cancer—represent the major causes of death in the developed world. Although massive efforts and investments have been made in cancer therapy, the progress made towards reducing mortality has been more successful for cardiovascular disease than for tumours. This can be attributable largely to an active prevention approach implemented for cardiovascular disease. Cardiologists treat their patients before the overt disease becomes life threatening, performing early interventions in phenotypically healthy patients, by using several markers that predict risk. If the concept of prevention could be applied to cancer in a more extensive way, a significant number of tumours could be avoided through preventive measures. Prevention approaches range from avoiding tobacco exposure to dietary strategies to active pharmacological approaches in higher risk groups. Host targets rather than the tumour cells themselves are attractive for chemoprevention, in particular endothelial and immune cells. Angioprevention i.e. preventing cancer angiogenesis is a key concept that we introduced; yet one of the major current challenges for anti-angiogenesis in therapy and prevention is finding the right biomarkers. Here we discuss the importance of angioprevention and the potential use of VEGF, PlGF, CD31, Ang and Tie, circulating vascular cell precursors, and microRNA as potential biomarkers.