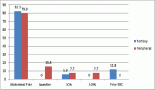
Osteosarcoma has the highest incidence among individuals of African descent, with growing evidence suggesting ethnic and racial genetic underpinning. Hence, it presents a grave public health challenge in Africa given the widening inequities in access to cancer care. This scoping review addresses the critical gap in the availability of locally relevant data on the magnitude of the burden and challenges relating to the management and outcome of African centres. This study included 1,374 patients from eighteen studies. 81% presented with locally advanced or metastatic disease. While surgical treatment for osteosarcoma is shifting toward limb salvage on a global scale, amputation remains preponderant in Africa as only 53% underwent limb salvage operations. The pooled 5-year overall survival was 49.1%. Late presentation, workforce and infrastructural shortage, cultural beliefs, patronage of unorthodox medicine practitioners and high healthcare costs were the barriers driving poor outcomes in African centres. Strategies to improve outcomes should focus on addressing these barriers.