Purpose: Cancer-related complications (CrC) and any potentially life-threatening findings detected on routine oncological imaging requires urgent intervention and needs proactive management. We conducted a retrospective study to highlight the role of imaging in the detection of CrC on computed tomography (CT)-scan while sharing our experience at a tertiary care cancer hospital.
Materials and methods: All the reports of the CT scans performed in our department between January 2018 and December 2019 were reviewed and the imaging findings of CrC were recorded. Only the patients who had known malignancy and underwent imaging evaluation at our centre at baseline/follow up/surveillance were included. The clinical details of the patients were recorded and the findings were classified based on the system or organ involved and also on the basis of its impact on clinical management.
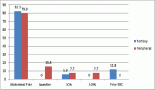
Results: A total of 14,226 CT scans were performed during the study period, out of which 599 patients had CrC. Most of the CrC were seen involving thorax (265/599, 44.3%) followed by abdomen (229/599, 38.2%) and head and neck (104/599, 17.3%) regions. The commonly encountered CrC were pulmonary infections, superior vena cava obstruction and drug-induced lung changes.
Conclusion: CrC have significant impact on the course of management of cancer patients and radiologist plays an important role in early diagnosis and initiation of prompt management of many such patients. CT is an excellent modality for early diagnosis of CrC which guides the oncologist for appropriate treatment.