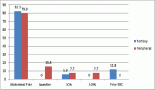
Ovarian cancer (OC) represents the most lethal malignancy in gynaecologic oncology practice and shows a high recurrence rate due to its early chemoresistance to first-line chemotherapy. Yet, timely selection of the correct treatment strategy is likely to prolong a patient’s survival. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of short non-coding RNAs responsible for the expression of 30%–60% of human genes. In numerous studies, miRNAs have been used to provide the overall prognosis for patients and analyse the process’s prevalence and responses to chemotherapy. In particular, miRNAs as markers for predicting the sensitivity of OC to platinum- and taxane-based chemotherapeutics can significantly improve the treatment efficacy. This article highlights two families of miRNAs: miR-200 and let-7, which are promising for further research on OC and its chemosensitivity.