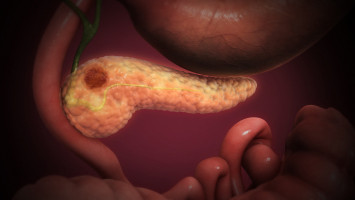
Cancer cells produce small amounts of their own form of collagen, creating a unique extracellular matrix that affects the tumour microbiome and protects against immune responses, according to a new study by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
This abnormal collagen structure is fundamentally different from normal collagen made in the human body, providing a highly specific target for therapeutic strategies.
This study, published today in Cancer Cell, builds upon previously published findings from the laboratory of Raghu Kalluri, MD, PhD, chair of Cancer Biology and director of operations for the James P Allison Institute, to bring a new understanding of the unique roles of collagen made by fibroblasts and by cancer cells.
"Cancer cells make an atypical collagen to create their own protective extracellular matrix that helps their proliferation and their ability to survive and repel T cells. It also changes the microbiome in a way that helps them thrive,” said Kalluri, senior author on the study. “Uncovering and understanding this unique adaptation can help us target more specific treatments to combat these effects.”
Type I collagen, the most abundant protein in the body, is produced by fibroblasts and found mostly in bones, tendons and skin.
Previously, collagen in tumours was believed to promote cancer development, but Kalluri’s laboratory showed that it likely plays a protective role in suppressing pancreatic cancer progression.
In its normal form, collagen is a heterotrimer consisting of two α1 chains and one α2 chain, which assemble to form a triple-helix structure as part of the extracellular matrix.
However, when studying human pancreatic cancer cell lines, the researchers discovered the cells expressed only the α1 gene (COL1a1), whereas fibroblasts expressed both genes.
Further analysis revealed that cancer cells have silenced the α2 gene (COL1a2) through epigenetic hypermethylation, resulting in a cancer-specific collagen ‘homotrimer’ made up of three α1 chains.
To investigate the real-world effects of this observation, the researchers created knockout mouse models of pancreatic cancer with COL1a1 deleted only in cancer cells.
Loss of this cancer-specific homotrimer reduced cancer cell proliferation and reprogrammed the tumour microbiome.
This led to lower immunosuppression, which was associated with increased T cell infiltration and elimination of cancer cells.
Additionally, these knockout mice responded more favourably to anti-PD1 immunotherapy, suggesting that targeting this cancer-specific collagen could help boost the anti-tumour immune response.
“This discovery illustrates the importance of mouse models, as it was only when we noticed a difference in their survival that we found this abnormal collagen variant existed and was produced specifically by the cancer cells,” Kalluri said. “Because it is generated in such small amounts relative to normal collagen, the homotrimer would have otherwise gone undetected without specific tools to differentiate them.”
Given the relationship between the gut and tumour microbiomes and immune responses, the researchers also explored the microbiome in their mouse models.
Interestingly, loss of the cancer-specific collagen led to changes in the bacterial composition within the tumour.
There was a corresponding decrease in myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and an increase in T cells, contributing to favourable survival outcomes.
These effects were completely reversed by disrupting the microbiome with antibiotics, suggesting that cancer-specific collagen promotes cancer progression by enhancing a tumour-promoting microbiome.
This is early evidence that the extracellular matrix directly influences the tumour microbiome, which could help researchers to understand how cancer cells have developed these adaptions against an immune response.
Further investigation clarified some of the mechanisms behind these findings, demonstrating that loss of the cancer-specific collagen increased levels of CXCL16, which attracts T cells, and reduced expression of CXCL5, which attracts MDSCs.
Loss of the collagen homotrimer also increased the amount of normal fibroblast collagen in the stroma, which, as Kalluri’s lab previously showed, inhibits tumour progression.
These results provide additional evidence that cancer-produced homotrimers affect signal pathways that can alter the tumour immune profile.
The study also found that the abnormal collagen upregulates signal pathways associated with cancer cell proliferation by binding to a surface protein called integrin α3.
Indeed, suppressing integrin α3 in vivo increased T cell infiltration and prolonged survival, highlighting this interaction as a very specific target for potential therapeutic strategies.
"No other cell in the normal human body makes this unique collagen, so it offers tremendous potential for the development of highly specific therapies that may improve patient responses to treatment,” Kalluri said. “On many levels, this is a fundamental discovery and a prime example of how basic science unravels important findings that could later benefit our patients.”
While the current study looked specifically at pancreatic cancer, Kalluri noted that collagen homotrimers also are seen in other cancer types, including lung and colon cancers, signifying a possible unifying principle with broad implications for cancer treatment.
The World Cancer Declaration recognises that to make major reductions in premature deaths, innovative education and training opportunities for healthcare workers in all disciplines of cancer control need to improve significantly.
ecancer plays a critical part in improving access to education for medical professionals.
Every day we help doctors, nurses, patients and their advocates to further their knowledge and improve the quality of care. Please make a donation to support our ongoing work.
Thank you for your support.